前言
Visualizing memory management in Golang
go 与常规 gc 语言的区别
- go 没有对内存 分代管理, The main reason for this is the TCMalloc(Thread-Caching Malloc), which is what Go’s own memory allocator was modeled upon. Many programming languages that employ Garbage collection uses a generational memory structure to make collection efficient along with compaction to reduce fragmentation. Go takes a different approach here, as we saw earlier, Go structures memory quite differently. Go employs a thread-local cache to speed up small object allocations and maintains scan/noscan spans to speed up GC. This structure along with the process avoids fragmentation to a great extent making compact unnecessary during GC.
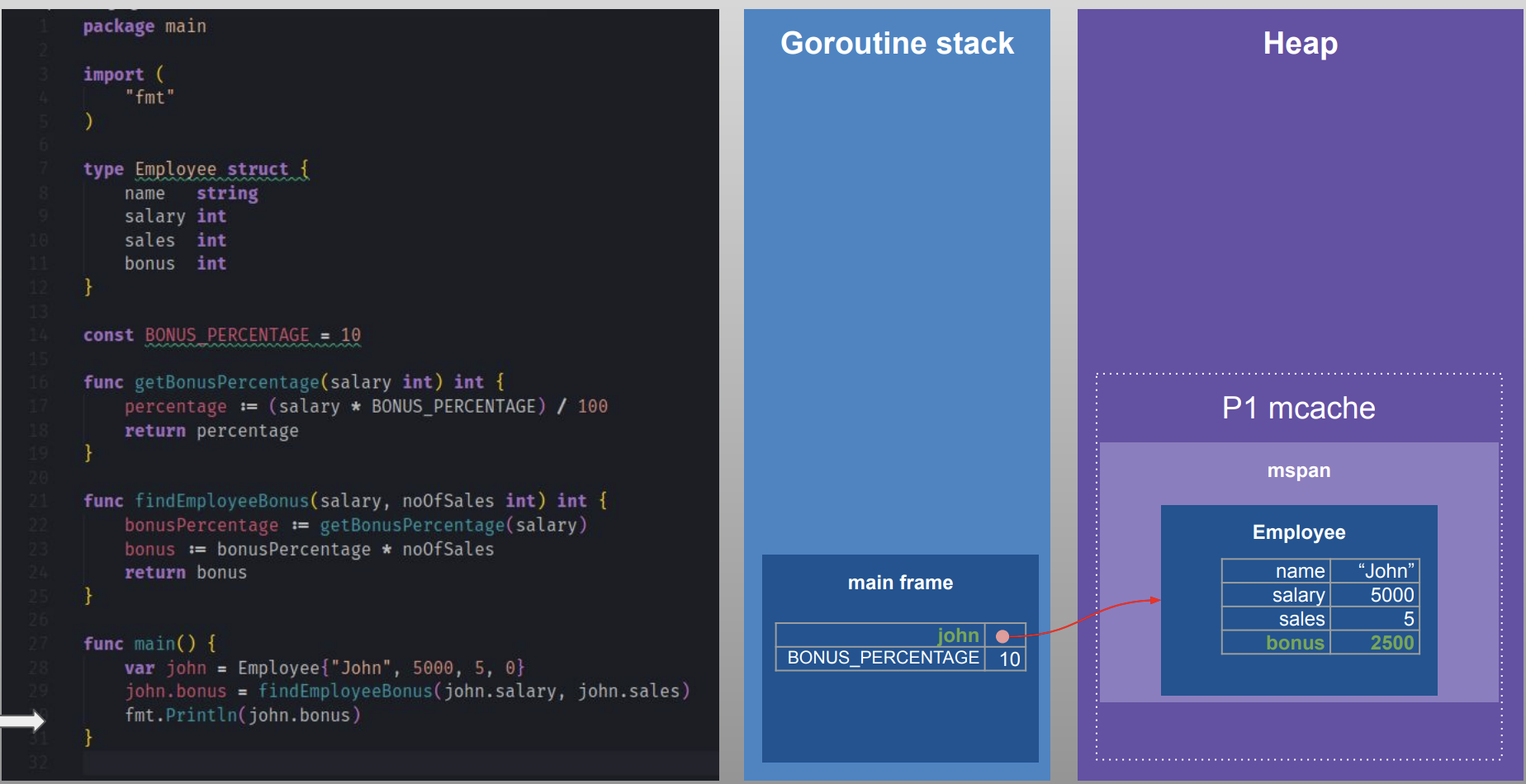
- One major difference Go has compared to many garbage collected languages is that many objects are allocated directly on the program stack. The Go compiler uses a process called escape analysis to find objects whose lifetime is known at compile-time and allocates them on the stack rather than in garbage-collected heap memory. During compilation Go does the escape analysis to determine what can go into Stack(static data) and what needs to go into Heap(dynamic data). Go的对象(即struct类型)是可以分配在栈上的。Go会在编译时做静态逃逸分析(Escape Analysis), 如果发现某个对象并没有逃出当前作用域,则会将对象分配在栈上而不是堆上,从而减轻了GC压力。其实JVM也有逃逸分析,但与Go不同的是Java无法在编译时做这项工作,分析是在运行时完成的,这样做一是会占用更多的CPU时间,二是不可能会把所有未逃逸的对象都优化到栈中。
内存分配算法 TCMalloc
在 TCMalloc 内存管理内部分为两个部分:线程内存(thread memory)和页堆(page heap)。
- 每一个线程都可以获得一个用于无锁分配小对象的缓存,这样可以让并行程序分配小对象(<=32KB)非常高效。PS, java 中叫TLAB:Thread Local Allocation Buffer
- TCMalloc 管理的堆由一组页组成,一组连续的页面被表示为 span。当分配的对象大于 32KB,将使用页堆(Page Heap)进行内存分配。
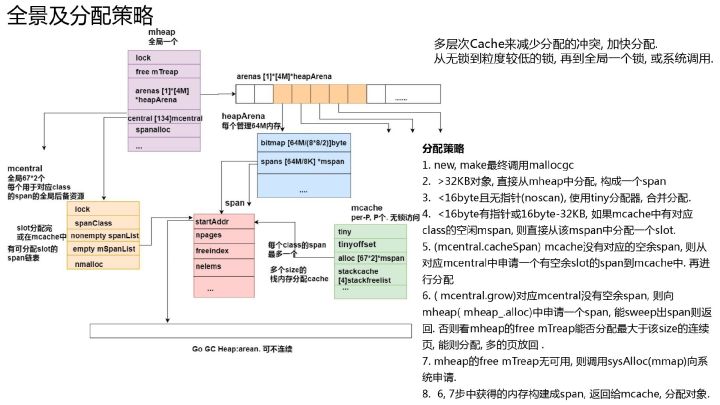
整体设计
Golang的内存分配器原理与tcmalloc类似,简单的说就是维护一块大的全局内存,每个线程(Golang中为P)维护一块小的私有内存mcache,私有内存不足再从全局申请。以64位系统为例,Golang程序启动时会向系统申请的内存如下图所示:
对象分配流程
A visual guide to Go Memory Allocator from scratch (Golang)Go 内存管理的一般思想是使用不同的内存结构为不同大小的对象使用不同的内存缓存级别来分配内存。将一个从操作系统接收的连续地址的块切分到多级缓存来减少锁的使用,同时根据object的大小分配内存减少内存碎片以提高内存分配的效率和在内存释放之后加快 GC 运行的速度。
- 大于 32K 的大对象直接从 mheap 分配。
- 小于 16B 的使用 mcache 的微型分配器分配
- 对象大小在 16B ~ 32K 之间的的,首先通过计算使用的大小规格,然后使用 mcache 中对应大小规格的块分配
- 如果对应的大小规格在 mcache 中没有可用的块,则向 mcentral 申请
- 如果 mcentral 中没有可用的块,则向 mheap 申请,并根据 BestFit 算法找到最合适的 mspan。如果申请到的 mspan 超出申请大小,将会根据需求进行切分,以返回用户所需的页数。剩余的页构成一个新的 mspan 放回 mheap 的空闲列表。
- 如果 mheap 中没有可用 span,则向操作系统申请一系列新的页(最小 1MB)。 Go 会在操作系统分配超大的页(称作 arena)。分配一大批页会减少和操作系统通信的成本。
go 内存分配器细节补充
堆上所有的对象都会通过调用 runtime.newobject 函数分配内存,该函数会调用 runtime.mallocgc 分配指定大小的内存空间。
// Allocate an object of size bytes.
// Small objects are allocated from the per-P cache's free lists.
// Large objects (> 32 kB) are allocated straight from the heap.
func mallocgc(size uintptr, typ *_type, needzero bool) unsafe.Pointer {
...
mp := acquirem()
var c *mcache
if mp.p != 0 {
c = mp.p.ptr().mcache // 获取当前的 G所属的P
} else {
c = mcache0
}
var span *mspan
if size <= maxSmallSize {
if noscan && size < maxTinySize { // Tiny allocator.
...
span = c.alloc[tinySpanClass]
v := nextFreeFast(span)
x = unsafe.Pointer(v)
...
}else{
...
span = c.alloc[spc]
v := nextFreeFast(span)
x = unsafe.Pointer(v)
...
}
}else{
...
span = largeAlloc(size, needzero, noscan)
x = unsafe.Pointer(span.base())
...
}
}
Go 语言的内存分配器包含内存管理单元runtime.mspan、线程缓存runtime.mcache、中心缓存runtime.mcentral和页堆runtime.mheap几个重要组件
type mspan struct {
next *mspan // next span in list, or nil if none
prev *mspan // previous span in list, or nil if none
startAddr uintptr // address of first byte of span aka s.base()
npages uintptr // number of pages in span
spanclass spanClass // size class and noscan (uint8)
...
}
type mcache struct {
// Tiny allocator
tiny uintptr
tinyoffset uintptr
local_tinyallocs uintptr
}
type mcentral struct {
lock mutex // 互斥锁
spanclass spanClass // span class ID
nonempty mSpanList // non-empty 指还有空闲块的span列表
empty mSpanList // 指没有空闲块的span列表
nmalloc uint64 // 已累计分配的对象个数
}
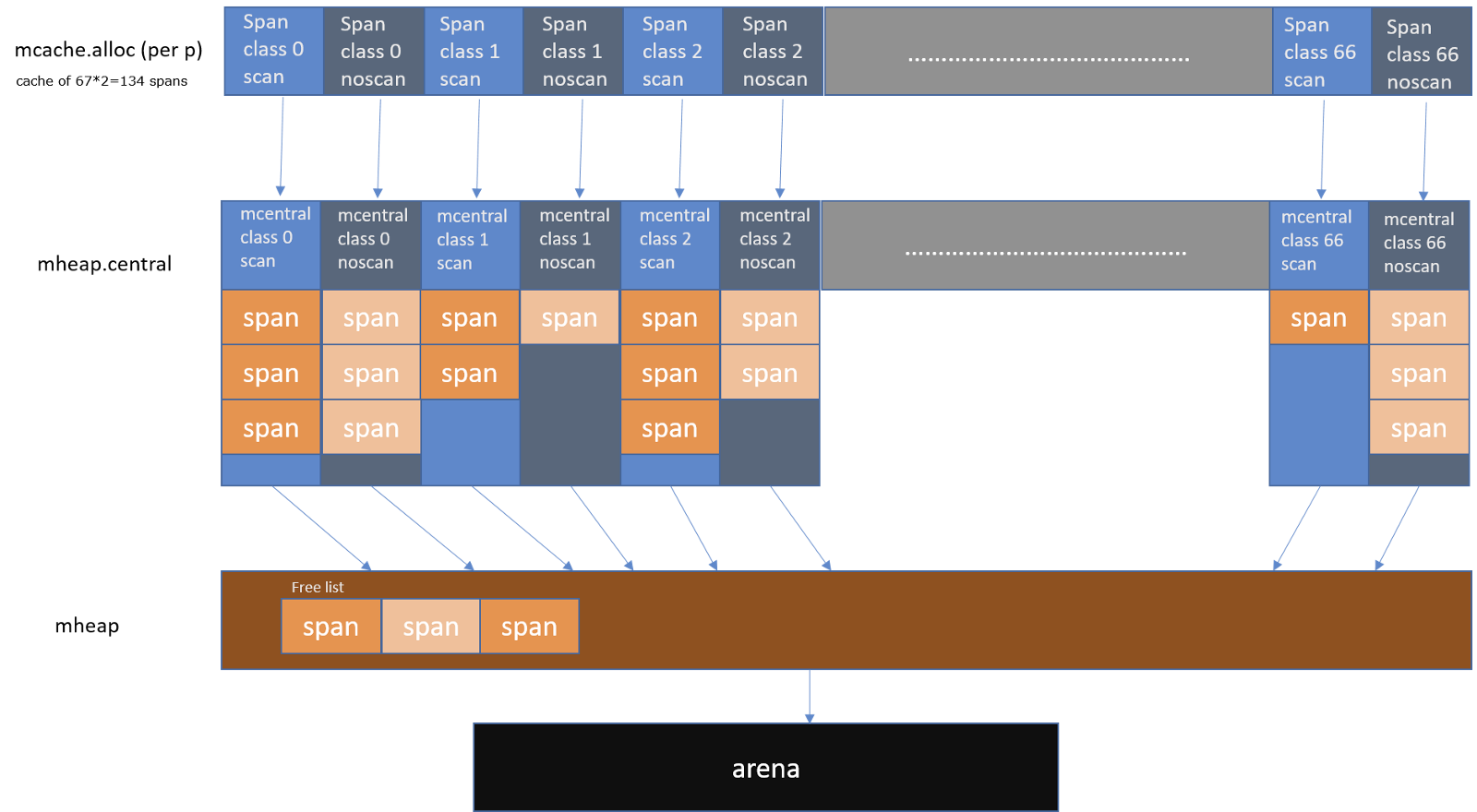
Golang为每个线程分配了span的缓存,即mcache,避免多线程申请内存时不断的加锁。当 mcache 没有可用空间时,从 mcentral 的 mspans 列表获取一个新的所需大小规格的 mspan。
从mcentral数据结构可见,每个mcentral对象只管理特定的class规格的span。事实上每种class都会对应一个mcentral
Go 使用 mheap 对象管理堆,只有一个全局变量(mheap 也是go gc 工作的地方)。持有虚拟地址空间。mheap 存储了 mcentral 的数组。这个数组包含了各个的 span 规格的 mcentral。由于我们有各个规格的 span 的 mcentral,当一个 mcache 从 mcentral 申请 mspan 时,只需要在独立的 mcentral 级别中使用锁,其它任何 mcache 在同一时间申请不同大小规格的 mspan 互不影响。
当 mcentral 列表为空时,mcentral 从 mheap 获取一系列页用于需要的大小规格的 span。
type mheap struct {
lock mutex
spans []*mspan
bitmap uintptr //指向bitmap首地址,bitmap是从高地址向低地址增长的
arena_start uintptr //指示arena区首地址
arena_used uintptr //指示arena区已使用地址位置
central [67*2]struct {
mcentral mcentral
pad [sys.CacheLineSize - unsafe.Sizeof(mcentral{})%sys.CacheLineSize]byte
}
}