前言
基本上静态分析可以做的事情,arthas 也做到了
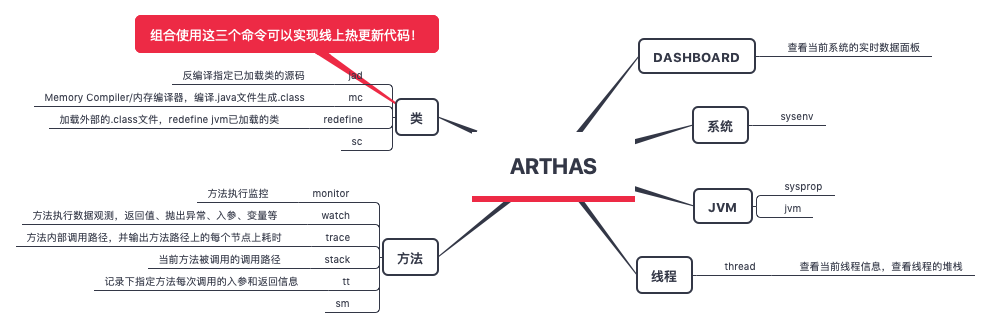
dashboard 与 JVM 运行指标
https://qiyeyun.gitbook.io/yyydata/jvm/jvm-yun-hang-zhi-biao
热更新代码
Step1 jad命令反编译到磁盘文件
jad --source-only demo.MathGame > /tmp/MathGame.java
Step2 使用文本编辑器修改代码
vi /tmp/MathGame.java
public static void print(int number, List<Integer> primeFactors) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer("" + number + "=");
Iterator<Integer> iterator = primeFactors.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
int factor = iterator.next();
sb.append(factor).append('*');
}
if (sb.charAt(sb.length() - 1) == '*') {
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
System.out.println("MyTest.......");
}
Step3 mc命令来内存编译修改过的代码
$ mc /tmp/MathGame.java -d /tmp
Memory compiler output:
/tmp/demo/MathGame.class
Step4 用redefine命令加载新的字节码
$ redefine /tmp/demo/MathGame.class
redefine success, size: 1
现在看一下程序日志
illegalArgumentCount:96218, number is: -169877, need >= 2
illegalArgumentCount:96219, number is: -57731, need >= 2
MyTest.......
illegalArgumentCount:96220, number is: -207843, need >= 2
illegalArgumentCount:96221, number is: -193695, need >= 2
MyTest.......
illegalArgumentCount:96222, number is: -19514, need >= 2
illegalArgumentCount:96223, number is: -199441, need >= 2
illegalArgumentCount:96224, number is: -110791, need >= 2
MyTest.......
illegalArgumentCount:96225, number is: -116154, need >= 2
MyTest.......
MyTest.......
MyTest.......
MyTest.......
MyTest.......
MyTest.......
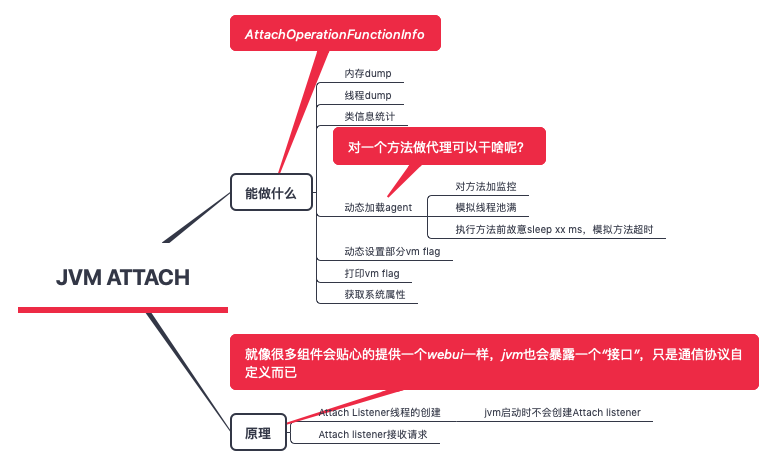
jvm attach 机制
JVM Attach机制实现Attach机制是jvm提供一种jvm进程间通信(这里用的是套接字socket)的能力,能让一个进程传命令给另外一个进程,并让它执行内部的一些操作。
static AttachOperationFunctionInfo funcs[] = {
{ "agentProperties", get_agent_properties },
{ "datadump", data_dump },
{ "dumpheap", dump_heap },
{ "load", JvmtiExport::load_agent_library },
{ "properties", get_system_properties },
{ "threaddump", thread_dump },
{ "inspectheap", heap_inspection },
{ "setflag", set_flag },
{ "printflag", print_flag },
{ "jcmd", jcmd },
{ NULL, NULL }
};
Attach_listener 线程的逻辑
static void Attach_listener_thread_entry(JavaThread* thread, TRAPS) {
...
for (;;) {
AttachOperation* op = AttachListener::dequeue();
...
// find the function to dispatch too
AttachOperationFunctionInfo* info = NULL;
for (int i=0; funcs[i].name != NULL; i++) {
const char* name = funcs[i].name;
assert(strlen(name) <= AttachOperation::name_length_max, "operation <= name_length_max");
if (strcmp(op->name(), name) == 0) {
info = &(funcs[i]);
break;
}
}
// check for platform dependent Attach operation
if (info == NULL) {
info = AttachListener::pd_find_operation(op->name());
}
if (info != NULL) {
// dispatch to the function that implements this operation
res = (info->func)(op, &st);
} else {
st.print("Operation %s not recognized!", op->name());
res = JNI_ERR;
}
// operation complete - send result and output to client
op->complete(res, &st);
}
}
- 从队列里不断取AttachOperation
- 根据 AttachOperation 得到 AttachOperationFunctionInfo
- 执行AttachOperationFunctionInfo 对应的方法并返回结果
一个网络问题排查
现象: rpc客户端read timeout。 那么问题可能出在网络层、rpc框架层和上层业务方
监控本机 eth0 网卡与目标主机的往来数据包tcpdump -i eth0 -nn 'host 目标主机ip'
可以观察到 在客户端数据发出后,服务端很快回复了ack,说明数据包顺利送达到了 服务端。但服务端的响应在很长时间之后才返回。 所以初步定位是服务端处理的问题
观察服务端日志,已知的业务日志收到请求的时间与 网络抓包的时间间隔很长(这里值得学习的一点就是网络抓包时间与 服务日志时间放在一起比对,以前没这么想过),基本可以判断问题出在 接收数据包与 框架调用业务逻辑之间,即出在框架层。
然后再使用arthas trace 指令跟踪框架层入口方法的执行逻辑,即可查看哪一个步骤执行的耗时时间最长。
