简介
镜像存储分为本地存储和Registry 存储,都是分层存储
- 本地存储,镜像下载到本地后,是如何在本地文件系统中存储的。以快速加载和启动容器为核心,容器在启动时需要将 镜像层按照顺序堆叠作为容器的运行环境,都是源文件(非压缩的)
- Registry 存储是指以什么方式存储在远端的 镜像仓库中。以方便镜像快速上传和拉取为核心,使用了压缩格式,按照layer 独立压缩和存储,使用镜像清单 manifest 包含所有的层,通过镜像摘要 digest 与tag 关联起来
最新进展 才云基于 Harbor 的企业级镜像仓库高可用实践
Docker registry,目前它更名为 Distribution。它做的主要事情就是把这些 images 按照 blob 一层一层地存到文件系统里面,每一个 blob 的 name 都是一长串的数字,这数字是根据文件的内容算出来的;甚至它一些描述信息,也是通过 blob 的方式存起来的。然后它提供了一套比较完备的 API 供你去调用,你可以知道这里面有哪些 image 是你可以 pull 或者 push
Harbor做的事情就是说它在原生的一个 Docker registry 的基础上提供了下面这些 features。所以先学习下registry 的基本原理很重要 关于docker image的那点事儿
- 图形界面
- Image Replication
- Access Control
- Operation Auditing,所有的操作都会有一个日志来记录
- Image Vulnerability Scanning,如果镜像里面 CentOS 有个漏洞,那么这个镜像在任何一个地方部署,漏洞也是一直存在的。
镜像仓库
联合文件系统是一种 堆叠文件系统,通过不停地叠加文件实现对文件的修改。其中,增加操作通过在读写层增加新文件实现,删除操作一般通过添加额外的删除属性文件实现,比如删除a.file时读写层增加一个a.file.delete文件。修改只读层文件时,需要先复制一份儿文件到读写层,然后修改复制的文件。PS:所以我们说镜像是一层层的,每个layer是什么呢? 一堆文件,比如a.file 和 b.file.delete 文件。
容器的rootfs 由多个layer 文件叠加而成,每个layer 文件在分发时都必须被打包成一个tar 文件(即a.file 和b.file.delete或whiteout标记 弄成一个文件),可选择压缩或非压缩的方式。打成一个文件的好处 除了发布方便,还可以生成摘要,便于校验和按内容寻址。
容器镜像包含以下的信息,镜像的4个部分之间通过digest 相互引用(内容寻址)
-
Manifest:包含特定平台、os的镜像信息、包含layer\config描述和digest信息
{ "schemaVersion":2, "config":{ "mediaType":"application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json", "size":6883, "digest": xx } "layers":[ { "mediaType":"application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json", "size":168654, "digest":xx }, { "mediaType":"application/vnd.oci.image.config.v1+json", "size":645724, "digest":xx }, ] } - Config:容器运行时需要用到的rootfs和执行参数
{ "author":xx, "os":"linux", "config":{ "ExposedPorts": { "8888/tcp":{} }, "Env":[], "Entrypoint":["/bin/myApp"], "Cmd":[ "-f", "/etc/harbor.cfg" ], "Volumes":{}, "Labels":{} }, "rootfs":{ "diff_ids":[ // 未压缩层文件的digest "sha256:xx", "sha256:xx" ], "type":"layers" }, "history":[] // 可选项 } - layer:包含了文件系统的信息,即该image包含了哪些文件/目录,以及它们的属性和数据。
- tar+gzip
docker manifest inspect istio/pilot:1.2.2 可以看到以下数据
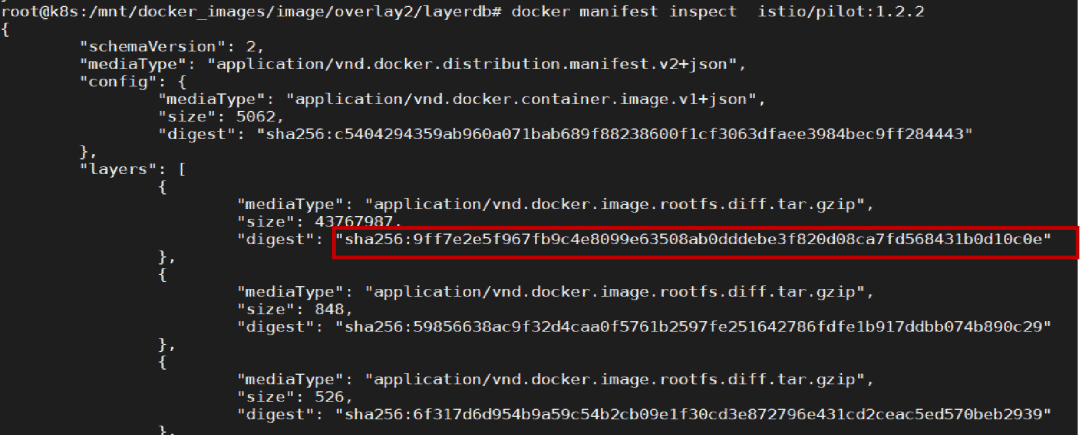
那镜像是如何下发的呢?
- 把tag解析为对应的manifest
- 获取manifest,查找本地不存在的层
- 下载层(tar.gz文件)
- 解压 通过解析镜像的格式以及下发过程,我们可以总结出影响镜像分发速度因素
- 镜像大小
- 网络带宽
- 并发数
- 有改动的层的大小
那如何加速镜像下发呢?
- 减少镜像层数,删除非必要文件
- 尽量使用相同的base image
- base镜像预拉取
- 多阶段构建
- 使用nginx 缓存
- 使用工具(如docker-slim)压缩镜像
- 后端使用对象存储
- Harbor replication,通过复制多个Harbor的方式,分担下载压力。
- 使用P2P协议,Dragonfly p2p;Uber Kraken p2p
image在docker registry 存储
DockOne技术分享(二十六):Docker Registry V1 to V2一个重要的视角,你可以观察registry daemon或container 在磁盘上的存储目录
| v1 | v2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 代码地址 | https://github.com/docker/docker-registry | https://github.com/docker/distribution |
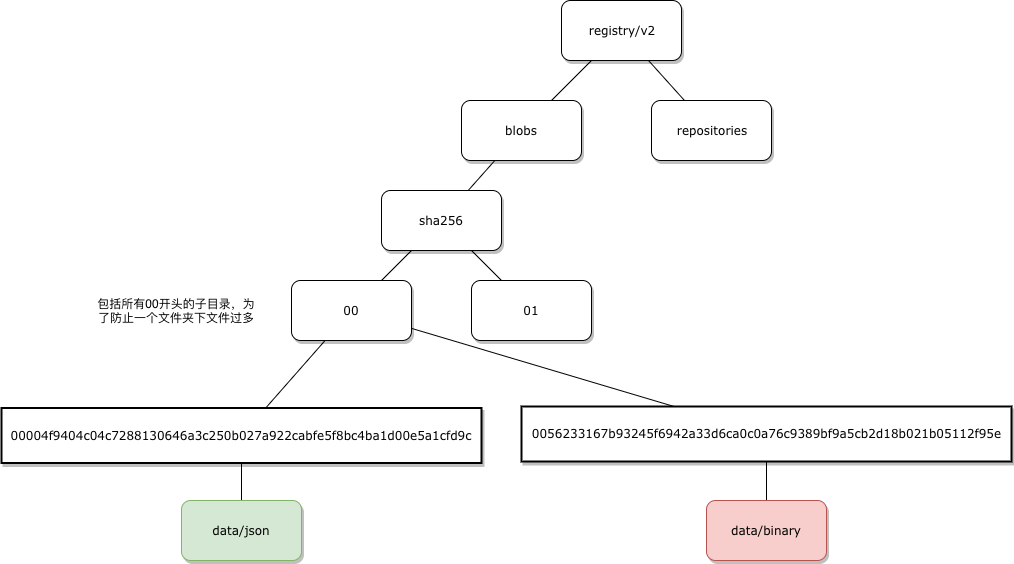
| 存储最上层目录结构 | images 和repositories | blobs 和 repositories |
| 最叶子节点 | layer 文件系统的tar包 Ancestry 父亲 layer ID |
data |
官方关于manifest 的解释Image Manifest Version 2, Schema 1
如何搭建私有镜像仓库执行 docker pull 实际上就是先获取到镜像的 manifests 信息,再拉取 blob。
api
汇总下来如下
- repository,经典存储库名称由2级路径构成,V2的api不强制要求这样的格式
- digest(摘要),摘要是镜像每个层的唯一标示
-
manifests
- v2 主要是提出了manifest, The new, self-contained image manifest simplifies image definition and improves security
- 一个docker image是由很多的layer组成,下载镜像时也是以layer为最小单元下载的。在v1的时代docker image,镜像结构有一种链表一样的组织,当下载完一个layer时,才能得到parent信息,然后再去下载parent layer。v2改变了这种结构,在image的manifest文件中存储了所有的layer信息,这样拿到所有的layer信息,就可以并行下载了
默认情况下,registry不允许删除镜像操作,需要在启动registry时指定环境变量REGISTRY_STORAGE_DELETE_ENABLED=true
源码分析
registry v2架构的的核心是一个web服务器,具体实现是用go语言的net/http包中的http.Server,在registry初始化时绑定了rest接口。请求会触发相应的handler,handler会从后端存储中取出具体的数据并写入response。
垃圾回收
In the context of the Docker registry, garbage collection is the process of removing blobs from the filesystem when they are no longer referenced by a manifest. Blobs can include both layers and manifests.
Filesystem layers are stored by their content address in the Registry. This has many advantages, one of which is that data is stored once and referred to by manifests.
Content Addressable Storage (CAS):Manifests are stored and retrieved in the registry by keying off a digest representing a hash of the contents. One of the advantages provided by CAS is security: if the contents are changed, then the digest no longer matches.
Layers are therefore shared amongst manifests; each manifest maintains a reference to the layer. As long as a layer is referenced by one manifest, it cannot be garbage collected.
Manifests and layers can be deleted with the registry API (refer to the API documentation here and here for details). This API removes references to the target and makes them eligible for garbage collection. It also makes them unable to be read via the API.
If a layer is deleted, it is removed from the filesystem when garbage collection is run. If a manifest is deleted the layers to which it refers are removed from the filesystem if no other manifests refers to them.
上文涉及到几个问题:
- image 是如在 docker distribution 上组织的?
- image 是分层的,所以image 肯定不是存储的最小单位,那是layer么?layer的存在形式是什么?image 和 layer之家的关系如何表示
- image 之间的依赖关系如何表示?
从这段话可以认为:
- image 在 docker distribution的表现形式为 manifest 和 blob,blob 包括manifest 和 layers,所以可以认为基本的存储是 manifest 和 layer
- manifest 和 layer 都有一个Content Address。layer 只存一份儿,可以被多个manifest 引用。只要还有一个 manifest 在引用layer, layer就不会被垃圾回收。 有点像jvm的垃圾回收和引用计数。
- registry API 中的删除 操作,是soft delete
- 对layer 来说, 是解除了 manifest 与layer的引用关系,使得layer 可以被删除
- 对manifest 来说,是解除了其与target的关系
- 真正物理删除要靠 garbage collection
对于docker 本地来说,可以通过docker rmi删除镜像,但对于docker distribition 来说,通过garbage collection 来防止镜像膨胀。
提炼一下
- 逻辑结构,一般体现逻辑概念:image,layer,manifest
- 物理结构,逻辑概念无关的通用概念 Blob,很多逻辑概念在存储上根本体现不到。以新的角度看数据结构 存储结构主要包括:顺序存储、链接存储、索引存储、散列存储 ,你光看存储结构根本就不知道树、图是什么鬼。
在v2 schema 下 逻辑结构
- layer是独立的,layer 之间不存在父子关系。layer 一以贯之的可以被多个image 共用。image 和 layer 之间是一对多关系
- 一对多关系由manifest 表述,一个manifest 可以视为一个image
存储结构
- Blob 是基本的存储单位,image 在存储结构上感知不到
- Blob 有两种形式,一个是文本(manifest json 字符串),一个是binary(tar.gz 文件)
harbor原理(待充实)
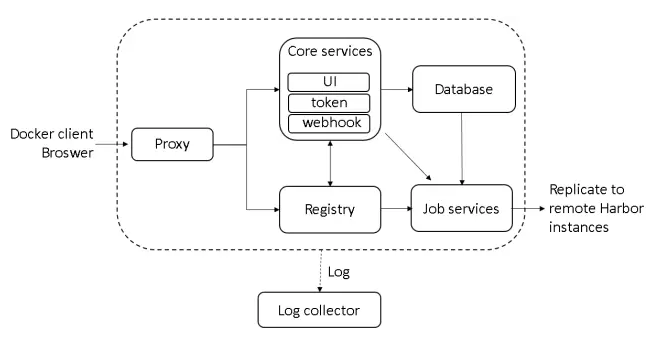
从架构上看,harbor 是基于 docker registry 做的。harbor做的一个核心的工作主要是 Core services 和 Job services 这两块
- Core services,提供ui 管理与权限控制
- Job services,镜像复制,镜像安全扫描等
其它
Deleting repositories First ,delete a repository in Harbor’s UI. This is soft deletion. Next, delete the actual files of the repository using the garbage collection in Harbor’s UI.
高可用可以做的一些思路:
- 有状态的话要挂盘,或者说用原生的一个集群来保证它的高可用;
- 那无状态的话,你要考虑是不是可以直接伸缩扩容,如果不能的话这个再另想办法。
碰到的问题
删除镜像
2018.12.7 harbor 1.4.0 版本
当你在ui 或者使用 registry restful api 删除某个layer时
- delete 操作只是软删,文件真正删除要等到gc 时
- delete 操作(甚至gc操作)后一段时间内,依然可以通过registry api 查到layer 信息,但无法真正下载
- GoogleContainerTools/jib 类的镜像制作工具push layer 时会先查询 layer 是否在registry 中存在,若存在则放弃push。
- 因为Content Addressable Storage (CAS),所以当你delete 某个镜像后,一样的内容再改个image名字 重新push 是没有用的(还是会拉不到image),因为Content Address 是一样的,Content Address 对应的manifest 还是被软删的状态,却被jib 视为已经存在。
无论新增还是删除镜像,harbor ui的展示都有延迟
