简介
火得一塌糊涂的kubernetes有哪些值得初学者学习的? Kubernetes 是透明的,它没有隐藏的内部 API。换句话说 Kubernetes 系统内部用来交互的 API 和我们用来与 Kubernetes 交互的 API 相同。这样做的好处是,当 Kubernetes 默认的组件无法满足我们的需求时,我们可以利用已有的 API 实现我们自定义的特性。
docker 安全
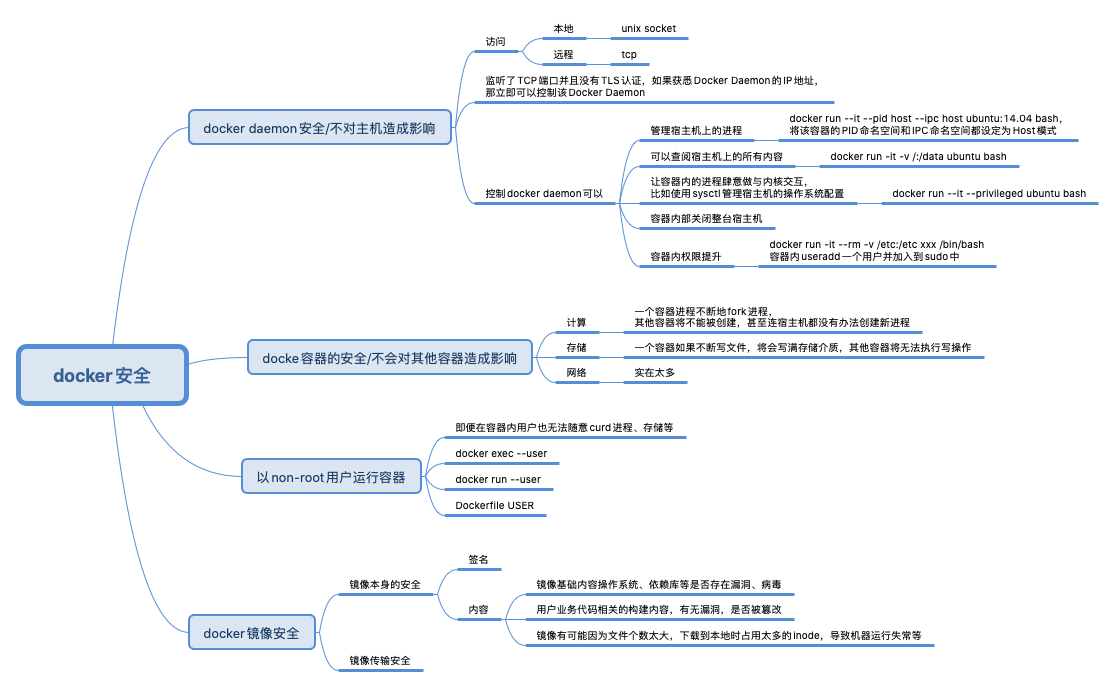
Docker 和 Kubernetes 中的 root 与 privileged--privileged 标志可以将我们前面看到的0的用户 ID 直接映射到主机的用户 ID 0上,使其可以不受限制地访问任何自己的系统调用。在正常的操作中,即使容器内有 root,Docker 也会限制容器的 Linux Capabilities 的,这种限制包括像 CAP_AUDIT_WRITE 这样的东西,
docker 多用户
理解 docker 容器中的 uid 和 gid默认情况下,容器中的进程以 root 用户权限运行,并且这个 root 用户和宿主机中的 root 是同一个用户。这就意味着一旦容器中的进程有了适当的机会,它就可以控制宿主机上的一切!
- 内核使用的是 uid 和 gid,而不是用户名和组名
- 可能会看到同一个 uid 在不同的容器中显示为不同的用户名
- 相同的 uid 不能有不同的特权,即使在不同的容器中也是如此
- docker 默认并没有启用 user namesapce,新创建的容器进程和宿主机上的进程在相同的 user namespace 中, docker 并没有为容器创建新的 user namespace
docker 启用user namesapce(此处只是普及,不推荐使用)
-
/etc/docker/daemon.json增加如下内容 并重启{ "userns-remap": "default" } - 没启用user namesapce 时,docker 拿root 来运行容器中进程。启用后, docker 拿什么用户来运行容器中进程呢?
- 启用user namesapce 后,docker daemon 会在宿主机上创建一个 dockremap 的用户
- 启动容器时,docker 会拿dockremap 的一个“从uid” 作为容器的root 用户来启动容器进程。该从uid 在容器内具有最高权限,在宿主机上具有和dockermap 一致的权限(操作宿主机volume 目录文件的时候)。PS:有点网络设备从设备的意思
多用户的使用
我们可以在 Dockerfile 中添加一个用户 dev,并使用 USER 命令指定以该用户的身份运行程序,Dockerfile 的内容如下:
FROM ubuntu
RUN groupadd -r dev && useradd -r -g dev dev
USER dev
ENTRYPOINT ["sleep", "infinity"]
则限定了 项目不能在随意位置 写日志,强制项目在 一个特定目录比如 /logs 下写日志(为dev 开放/logs目录写权限),并将/logs 映射到物理机的某个目录,定期整理/logs 目录即可。
但该方案带来的问题是:对项目限制比较大,需要一个完备的白名单,理论上不能限制项目对磁盘目录的读写。
概念
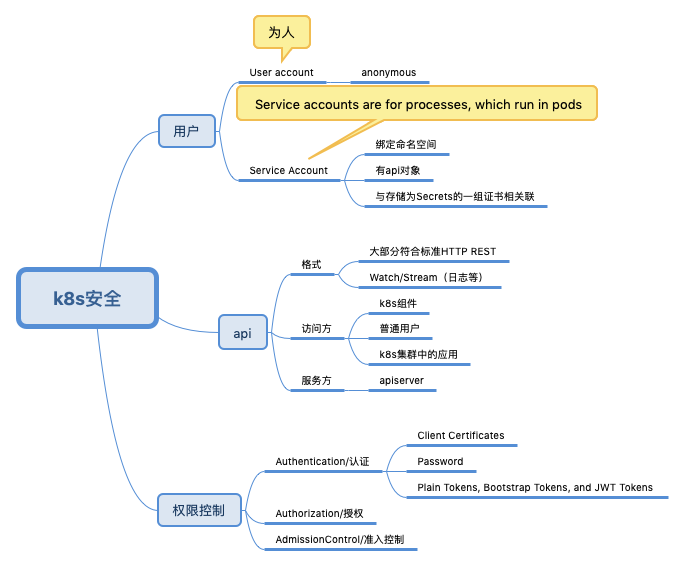
用户
- User accounts are for humans. Service accounts are for processes, which run in pods.
- User accounts are intended to be global. Names must be unique across all namespaces of a cluster, future user resource will not be namespaced. Service accounts are namespaced.
access the API
客户端和 API Server 作为通信的普 通参与者,各有一张证书。而这两张证书,都是由 CA 签发。客户端信任集群 CA,所以它信任拥有集群 CA 签发证书的 API Server;反过来 API Server 需要信任客户端 CA,它才愿意与客户端通信。
Controlling Access to the Kubernetes API
- Authentication:即身份验证,这个环节它面对的输入是整个http request。它负责对来自client的请求进行身份校验,支持的方法包括:client证书验证(https双向验证)、basic auth、普通token以及jwt token(用于serviceaccount)。APIServer启动时,可以指定一种Authentication方法,也可以指定多种方法。如果指定了多种方法,那么APIServer将会逐个使用这些方法对客户端请求进行验证,只要请求数据通过其中一种方法的验证,APIServer就会认为Authentication成功;
- Authorization:授权。这个阶段面对的输入是http request context中的各种属性,包括:user、group、request path(比如:/api/v1、/healthz、/version等)、request verb(比如:get、list、create等)。APIServer会将这些属性值与事先配置好的访问策略(access policy)相比较。APIServer支持多种authorization mode,包括AlwaysAllow、AlwaysDeny、ABAC、RBAC和Webhook。APIServer启动时,可以指定一种authorization mode,也可以指定多种authorization mode,如果是后者,只要Request通过了其中一种mode的授权,那么该环节的最终结果就是授权成功。
- Admission Control:从技术的角度看,Admission control就像a chain of interceptors(拦截器链模式),它拦截那些已经顺利通过authentication和authorization的http请求。http请求沿着APIServer启动时配置的admission control chain顺序逐一被拦截和处理,如果某个interceptor拒绝了该http请求,那么request将会被直接reject掉,而不是像authentication或authorization那样有继续尝试其他interceptor的机会。
安全相关的 kubernetes objects
Secrets——非明文的configmap
- 为什么弄一个Secrets?
- 其它组件(主要是Pod)如何获取Secrets数据?
为什么要弄一个Secrets? 回答为什么的一般方法是:对比前后差异。
Kubernetes secret objects let you store and manage sensitive information, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and ssh keys. Putting this information in a secret is safer and more flexible than putting it verbatim(原样的) in a Pod Lifecycle definition or in a container image . 管理敏感信息,如果没有Secrets,这些信息可能被保存在 pod 定义或者 docker 镜像中,有信息泄露的风险(PS:笔者曾把密码写在代码测试类里提交到公司仓库, 结果被几个看源码的小哥发现并使用了)
K8s Secrets 中保存的数据都必须经过 base64加密
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: db-secret
type: Opaque
data:
# base64
carrot-db-username: Y2Fycm90
carrot-db-password: Y2Fycm90
Secrets can be mounted as data volumes or be exposed as environment variables to be used by a container in a pod
- volume 方式, Each key in the secret data map becomes the filename under mountPath. 每一个secret key 会变成 container mountPath 下的一个文件。When a secret being already consumed in a volume is updated, projected keys are eventually updated as well. Kubelet is checking whether the mounted secret is fresh on every periodic sync. 当你改了secret 数据,则容器内的文件内容也能自动同步
- Environment Variables
Service Accounts——让pod 可以访问apiserver
配置 Pod 的 Service Account service account 只是提供了一个类似用户名的标识,真正ServiceAccount 有哪些权限要 通过 ClusterRoleBinding 绑定 ClusterRole。
A service account provides an identity for processes that run in a Pod. When you (a human) access the cluster (for example, using kubectl), you are authenticated by the apiserver as a particular User Account (currently this is usually admin, unless your cluster administrator has customized your cluster). Processes in containers inside pods can also contact the apiserver. When they do, they are authenticated as a particular Service Account (for example, default).
为什么弄一个Service Accounts?为processes (that run in a Pod) 提供必要的身份认证
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
namespace: mynamespace
name: example-sa
Kubernetes 会为一个 ServiceAccount自动创建并分配一个 Secret 对象,secret {data.token} 就是用户 token 的 base64 编码,可以用来配置kubeconfig
$ kubectl get sa -n mynamespace -o yaml
- apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
creationTimestamp: 2018-09-08T12:59:17Z
name: example-sa
namespace: mynamespace
resourceVersion: "409327"
...
secrets:
- name: example-sa-token-vmfg6
$ k describe secret example-sa-token-vmfg6
Name: example-sa-token-vmfg6
Namespace: mynamespace
Labels: <none>
Annotations: kubernetes.io/service-account.name: example-sa
kubernetes.io/service-account.uid: 0fc75075-41b9-48e5-af75-c1b31d64955b
Type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
Data
====
ca.crt: 1346 bytes
namespace: 11 bytes
token: xx # base64 编码,反解析后是一个json
用户的 Pod可以声明使用这个 ServiceAccount
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
namespace: mynamespace
name: sa-token-test
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.7.9
serviceAccountName: example-sa
等这个 Pod 运行起来之后,我们就可以看到,该 ServiceAccount 的 token,也就是一个 Secret 对象,被 Kubernetes 自动挂载到了容器的 /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount 目录下
$ kubectl describe pod sa-token-test -n mynamespace
Name: sa-token-test
Namespace: mynamespace
...
Containers:
nginx:
...
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from example-sa-token-vmfg6 (ro)
小结一下
- 有哪些资源
- Role 表述对这些资源的操作能力
- User/ServiceAccount 和 Role 绑定在一起,进而拥有Role 所具有的能力
- Pod 和 ServiceAccount 绑定在一起, Pod内进程可以使用 k8s push到本地的ServiceAccount 数据访问 api resource
