简介
本文主要来自陈皓 的两篇文章 以及付费专栏《左耳听风》,作者的水平很高,语句也很精炼,实在是没什么可提炼整理的,干脆就弄成读书笔记了。
编程的本质
两篇论文
Algorithms + Data Structures
- 如果数据结构设计的好,算法会简单
- 好的通用算法 应该用在不同的数据结构上
An algorithm can be regarded as consisting of a logic component, which specifies the knowledge to be used in solving problems, and a control component, which determines the problem-solving strategies by means of which that knowledge is used. The logic component determines the meaning of the algorithm whereas the control component only affects its efficiency. The efficiency of an algorithm can often be improved by improving the control component without changing the logic of the algorithm. We argue that computer programs would be more often correct and more easily improved and modified if their logic and control aspects were identified and separated in the program text.
Algorithm = Logic + Control
- Logic 解决问题
- Control 只影响效率
- Logic 和 Control 没有关系
- Logic 和 Control 如果分开,代码更容易改进和维护
算法的效率往往可以通过提高控制部分的效率来实现,而无须改变逻辑部分
吴翰清(道哥)眼中的机器智能:计算机的再发展在计算机的发展历史中,冯诺依曼提出了两项技术的关键性改进,第一,由二进制代替了十进制;第二,将程序和数据放到了存储器。当时世界上第一台计算机是由电子管制成的,需要通过大量的外部电路进行控制。冯诺依曼是第一个提出电路设计和逻辑设计是应该分离的,这是思想上的巨大进步。
揉和一下
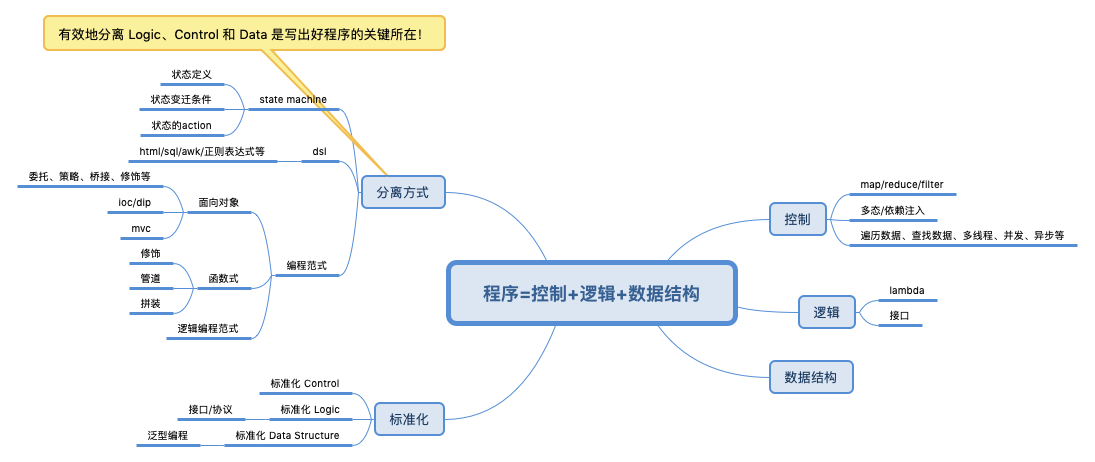
-
算法的效率往往可以通过提高控制部分的效率来实现,而无须改变逻辑部分。就像函数式编程中的 Map/Reduce/Filter,它们都是一种控制。而传给这些控制模块的那个 lambda 表达式才是我们要解决的问题的逻辑,它们共同组成了一个算法。最后,我再把数据放在数据结构里进行处理,最终就成为了我们的程序。
- 控制一个程序流转的方式,即程序执行的方式,并行还是串行,同步还是异步,以及调度不同执行路径或模块,数据之间的存储关系,这些和业务逻辑没有关系。
-
代码复杂度的本质:
- 业务逻辑的复杂度决定了代码的复杂度;
- 控制逻辑的复杂度 + 业务逻辑的复杂度 ==> 程序代码的混乱不堪;
- 绝大多数程序复杂混乱的根本原因:业务逻辑与控制逻辑的耦合。
程序的本质复杂性和元语言抽象
- 逻辑就是问题的定义,比如,对于排序问题来讲,逻辑就是“什么叫做有序,什么叫大于,什么叫小于,什么叫相等”?控制就是如何合理地安排时间和空间资源去实现逻辑。比如java collections 的sort 方法
public static <T> void sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> comparator) - 如果目标还是代码“简短、优雅、易理解、易维护”,那么代码优化是否有一个理论极限?这个极限是由什么决定的?普通代码比起最优代码多出来的“冗余部分”到底干了些什么事情?程序的本质复杂性就是逻辑,非本质复杂性就是控制。逻辑决定了代码复杂性的下限,也就是说不管怎么做代码优化,Office程序永远比Notepad程序复杂,这是因为前者的逻辑就更为复杂。如果要代码简洁优雅,任何语言和技术所能做的只是尽量接近这个本质复杂性,而不可能超越这个理论下限。
- 理解”程序的本质复杂性是由逻辑决定的”从理论上为我们指明了代码优化的方向:让逻辑和控制这两个维度保持正交关系。绝大多数程序不够简洁优雅的根本原因:逻辑与控制耦合
- 每种组件形式都代表了特定的抽象维度,组件复用只能在其维度上进行抽象层次的提升。比如,我们可以把常用的HashMap等功能封装为类库,但是不管怎么封装复用类永远是类,封装虽然提升了代码的抽象层次,但是它永远不会变成Lambda,而实际问题所代表的抽象维度往往与之并不匹配。
-
逻辑决定了程序的本质复杂性,但接口不是表达逻辑的通用方式,那么是否存在表达逻辑的通用方式呢? 通过元语言抽象让逻辑和控制彻底解耦!有两种方式:元编程(比如thrift、定义了thrift文件,并提供一个thrfit 编译器);元驱动编程,类似于下文的通用检查用户注册信息的逻辑。那么我们编写代码时,如何从业务中发现“元”(逻辑),是一个很有意义的问题,可以从
Collections.sort(xx,comparator)开始。var meta_create_user = { form_id : 'create_user', fields : [ { id : 'name', type : 'text', min_length : 3 }, { id : 'password', type : 'password', min_length : 8 }, { id : 'repeat-password', type : 'password', min_length : 8 }, { id : 'email', type : 'email' } ] };
陈皓在给《代码整洁之道》中的序文提到:无论微观世界的代码,还是宏观层面的架构,无论是三种编程范式还是微服务架构,它们都在解决一个问题:分离控制和逻辑。所谓控制,就是对程序流转的与业务无关的代码或系统的控制(如多线程、异步、服务发现、部署、弹性伸缩等),所谓逻辑则是实实在在的业务逻辑,是解决用户问题的逻辑。控制和逻辑控制了整体的软件复杂度,有效的分离控制和逻辑会让你的系统得到最大的简化。
编程哲学
Design GuidelinesYou must develop a design philosophy that establishes a set of guidelines. This is more important than developing a set of rules or patterns you apply blindly. Guidelines help to formulate, drive and validate decisions. You can’t begin to make the best decisions without understanding the impact of your decisions. Every decision you make, every line of code you write comes with trade-offs. 做任何事都是这样。
Philosophy 要删减
- Prepare Your Mind 有感觉但感触不深,建议看原文
- Reading Code. Code is read many more times than it is written.
- Legacy Software. There are many reasons why programs are built the way they are, although we may fail to recognize the multiplicity of reasons because we usually look at code from the outside rather than by reading it. When we do read code, we find that some of it gets written because of machine limitations, some because of language limitations, some because of programmer limitations, some because of historical accidents, and some because of specifications—both essential and inessential. - Gerald M. Weinberg 你有很多理由堆很多代码,必要也不必要
- Mental Models. You must constantly make sure your mental model of your projects are clear. When you can’t remember where a piece of logic is or you can’t remember how something works, you are losing your mental model of the code. This is a clear indication that refactoring is a must. Focus time on structuring code that provides the best mental model possible and code review for this as well. 当你看不懂代码的时候,就是该你重构的时候。Everyone knows that debugging is twice as hard as writing a program in the first place. So if you’re as clever as you can be when you write it, how will you ever debug it?
- Correctness vs Performance. Make it correct, make it clear, make it concise, make it fast. In that order. - Wes Dyer
- Productivity vs Performance. “Making things easy to do is a false economy. Focus on making things easy to understand and the rest will follow.” - Peter Bourgon 不要去写最容易写的代码,去写最容易懂的代码。
This is about writing simple code that is easy to read and understand without the need of mental exhaustion. Just as important, it’s about not hiding the cost/impact of the code per line, function, package and the overall ecosystem it runs in.
You must be aware of who you are on your team. When hiring new people, you must be aware of where they fall. The code must be written for the average developer to comprehend. If you are below average, you have the responsibility to come up to speed. If you are the expert, you have the responsibility to reduce being clever.
“Encapsulation and the separation of concerns are drivers for designing software. This is largely based on how other industries handle complexity. There seems to be a human pattern of using encapsulation to wrestle complexity to the ground.” 抽象和封装驱动了软件的设计
“Programmers waste enormous amounts of time thinking about, or worrying about, the speed of noncritical parts of their programs, and these attempts at efficiency actually have a strong negative impact when debugging and maintenance are considered. We should forget about small efficiencies, say about 97% of the time: premature optimization is the root of all evil. Yet we should not pass up our opportunities in that critical 3%.” — Donald E. Knuth
Data-Oriented Design:”Data dominates. If you’ve chosen the right data structures and organized things well, the algorithms will almost always be self-evident. Data structures, not algorthims, are central to programming.” - Rob Pike
其它
程序员如何把控自己的职业只有学会总结和归纳,才能形成自己的思维框架、自己的套路、自己的方法论,以后学这个东西应该怎么学。就像学一门新的语言,不管GO语言,还是Rust语言,第一件事情就是了解内存是怎么管理的,数据类型什么样,第二是泛型怎么搞,第三是并发怎么弄。还有一些抽象怎么弄,比如说怎么解耦,怎么实现多态?套路这种东西只有学的多了以后才能形成套路,如果你只学会一门语言不会有套路,你要每年学门语言,不用学多精,你思考这个语言有什么不一样,为什么这个这种有玩法,那个有那种玩法,这些东西思考多了套路方法论就出来了。
十个有用的软件开发原则代码可以被丢掉重写,但数据很少会这样。数据比代码更重要。代码的唯一目的是转换数据。在设计新系统时,最好先从数据库和数据结构开始,并在此基础上开发代码。要考虑可以在数据上施加的约束并实施它们,理想情况下是通过表示数据的方式进行的。代码设计是数据设计的下一步。数据模型越简单、越一致,代码就会越简单。
你们把流程图给我看,但把表藏起来,我就一头雾水。你们把表给我看,通常我就不需要你们的流程图,它们会不言自明。—— Fred Brooks
糟糕的程序员关心代码。好的程序员关心数据结构和它们之间的关系。—— Linux 之父 Linus Torvalds
